The Battle of SSD and RAM: A Comprehensive Guide
Did you know that StorageTeK invented the first version of SSD in 1978? Since then, these storage devices have been widely used in computers and laptops. But what is the difference between RAM and SSD? Does it do anything to your PC speed or performance?
Whatever your questions might be, we will answer all of them today in this comprehensive guide, including what is SSD and RAM and their key differences. Read this article until the end to learn more about this topic.
What is an SSD?
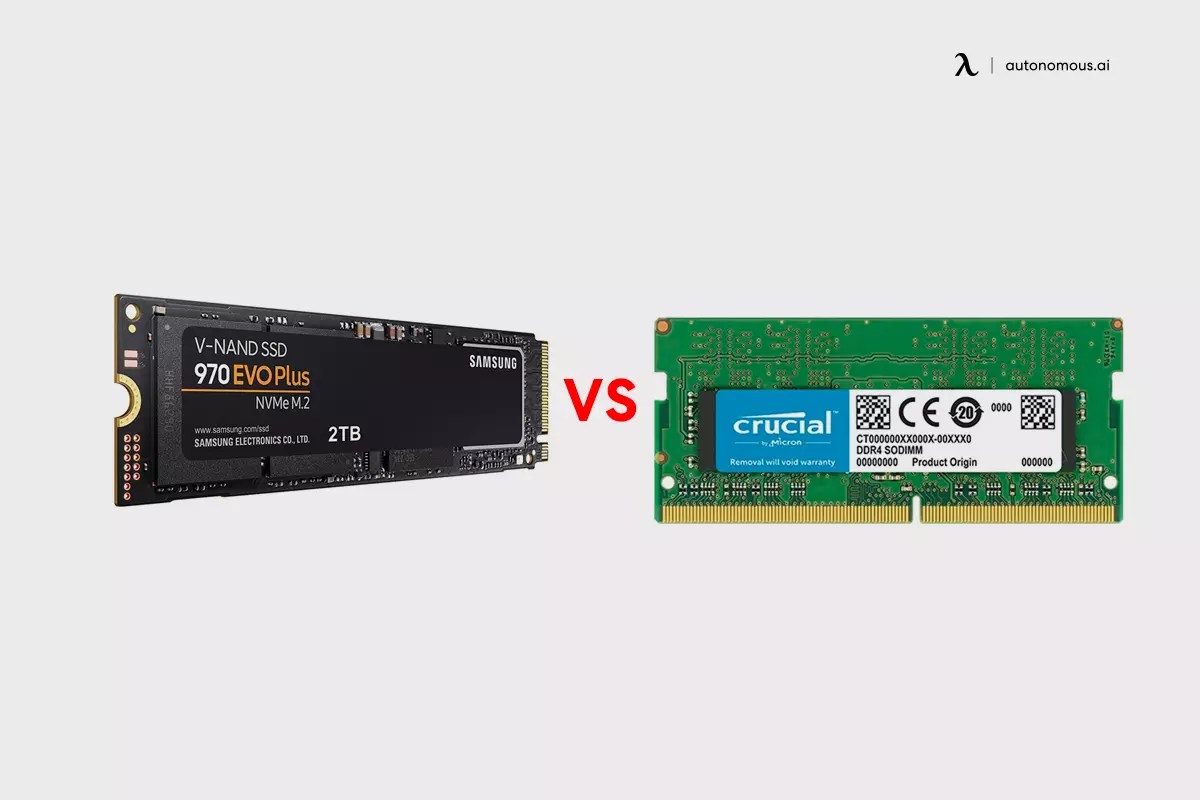
SSD stands for a solid-state drive. This type of non-volatile flash memory is actively used in computers and laptops for permanent storage. SSD has become quite popular lately, more than its predecessor, HDD.
HDD, a hard disk drive, is also a permanent storage drive that uses a spinning magnetic disk to write and transfer information. However, the moving parts led to wear and tear heating and slow data processing function. SSD, as good news, does not have any moving parts.
A tech-savvy person knows SSD is better than HDD in speed and efficiency, and SSD greatly improves your computer's overall performance and speed. A PC using an SSD is just like a system of steroids compared to one using an HDD.

What is RAM?
RAM stands for random access memory, a flash memory that the computer uses to store session-specific data and information. It is volatile storage, meaning that the information it stores is limited to the extent it remains on. When your system turns off, the RAM is cleared and empty.
SSD vs. RAM – What is the Difference?
People interested in tech gadgets probably know the difference between SSD and RAM. First, talking about the similarities, we know that SSD and RAM are both storage devices that store data on your computer. These are two types of computer memories, also known as the brains of the computer.
The main difference between RAM and SSD is the volatility. RAM is a volatile memory storage option, as the stored data is wiped out when the computer powers down. An SSD, on the other hand, is a permanent storage device.
Here's a table comparing SSD (Solid State Drive) and RAM (Random Access Memory):
| Criteria | SSD (Solid State Drive) | RAM (Random Access Memory) |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Long-term storage of data and files, retains data even when the computer is turned off | Temporary storage for data currently being used or processed by the CPU |
| Data Persistence | Non-volatile; retains data permanently until deleted or overwritten | Volatile; data is lost when the computer is turned off |
| Speed | Fast read/write speeds, significantly faster than traditional HDDs, but slower than RAM | Extremely fast data access speeds, much faster than SSDs |
| Capacity | Typically ranges from 128GB to several terabytes (TB) | Typically ranges from 4GB to 64GB or more in high-end systems |
| Usage | Storing operating systems, applications, files, and other long-term data | Running applications, processes, and active tasks; temporary workspace for the CPU |
| Impact on Performance | Improves boot times, application loading, and file transfer speeds | Directly impacts the speed and performance of running applications and multitasking |
| Form Factor | Available in various form factors (e.g., 2.5-inch, M.2, PCIe) | Typically in DIMM (Desktop) or SO-DIMM (Laptop) form factors |
| Power Consumption | Low power consumption compared to HDDs | Low power consumption, essential for maintaining data during operation |
| Durability | More durable than HDDs, no moving parts, less prone to physical damage | Durable, but susceptible to electrostatic discharge (ESD) damage |
| Upgrade Impact | Upgrading improves storage capacity and can enhance overall system speed | Upgrading improves multitasking ability and overall system responsiveness |
| Cost | More expensive per gigabyte compared to HDDs, but prices are decreasing | Generally less expensive per gigabyte compared to SSDs, but total cost varies by capacity |
| Lifespan | Limited write cycles, though modern SSDs have improved longevity | Generally long-lasting, but can degrade with extensive usage |
FAQs
1. How Much RAM and SSD Do I Need?
Generally speaking, the amount of RAM and SSD you need depends on the tasks you wish to complete on your system. If you have a system just for normal office work, without any special requirements, you can easily work on 6 GB RAM and 128 GB SSD. You can even work on HDD perfectly if you wish so.
However, for high-level tasks such as gaming and video editing, at least 8 to 12 GB of RAM with SSD starting from 512 GB is required. The better these two storage options, the better functioning your PC is.
2. Is 8GB RAM and 256GB SSD Enough?
As we said earlier, SSD to RAM requirements depend on what types of tasks you wish to accomplish. In most cases, these specs are enough for a normal computer user, allowing you to complete tasks seamlessly. However, you will need some better specs for gaming and other needs.
3. Can an SSD Increase My RAM?
No. There is no direct relationship between SSD and RAM. Increasing SSD does not affect your PC's RAM, and RAM means how much volatile memory you have and how good your multitasking capacity is. On the other hand, an SSD is a permanent storage device that processes data.
4. How Does RAM Affect Computer Speed?
RAM is volatile memory, exposed to an enormous amount of data that it needs to process on the go. Speed and latency are the most important factors when it comes to RAM. For a computer setup with high RAM, the system can quickly process high amounts of data, resulting in a smooth experience.
The high amount of RAM allows you to multitask effectively with numerous applications open simultaneously, thanks to the high information processing capacity of the memory. Upgrading your computer RAM will speed up your computer using experience and your ability to multitask.
Most computers use DDR4 RAM slots that allow you to install an additional RAM stick, solely based on your decision. Consider factors such as CAS latency and other technical specifications before performing the upgradation process. The computer guy will tell you exactly what is compatible with your PC.
5. Does an SSD Make the Computer Fast?
Shifting from the HDD to SSD is like installing a Ferrari instead of a Toyota engine, and the results are immense. There is no clear comparison when we talk about SSD vs. RAM speed, as both memory devices are used for different purposes, and using SSD as RAM is also a misty concept.
However, SSDs make your system faster because they read and write data faster than HDDs. This allows your computer to process information at a bullet's pace, increasing your overall efficiency and effectiveness.

6. How Much is a PC with High RAM and SSD Storage?
A system with PC accessories, such as a high amount of RAM and SSD storage, costs relatively higher than a system with less RAM and HDD. SSD is a clear storage device winner when it comes to non-volatile storage, and this is due to its fast reading and writing capability. On the other hand, RAM determines how much data a system can process and how well multitasking is done.
There is no clear answer if we talk about how much a PC is; it depends on how much RAM is installed and the size of the non-volatile memory stored in the system.
7. Unified memory vs SSD storage: What’s the difference?
Unified memory combines system RAM and GPU memory into one shared pool for faster data access, mainly in Apple’s M-series chips. SSD storage, on the other hand, is permanent storage for files and applications. Unified memory directly affects active performance, while SSD improves boot and load times.
8. Memory SSD vs HDD: Which should I choose?
SSD is much faster, more durable, and uses less power compared to HDD. HDD may be cheaper for large capacity, but SSD is better for speed, reliability, and modern systems.
9. Difference between RAM and SSD: How do they compare?
RAM is temporary memory for active processes, while SSD is permanent storage for files and the operating system. RAM impacts multitasking speed, SSD impacts boot and load times.
10. 8GB RAM vs 16GB RAM: Which is better?
8GB RAM is sufficient for light use such as office tasks and browsing. 16GB RAM is better for gaming, video editing, or multitasking with many applications open.
11. Memory vs SSD storage: Do I need both?
Yes, memory (RAM) and SSD storage work together. RAM handles active tasks, while SSD stores your system and files. Both are essential for a balanced, responsive PC.
12. Speed of RAM vs SSD: Which is faster?
RAM is significantly faster than SSD, with near-instant access speeds. SSDs are still faster than HDDs, but RAM remains the quickest memory type in a PC.
13. 2GB RAM vs 4GB RAM: Is there a big difference?
Yes. 2GB RAM is now very limited, only suitable for basic tasks. 4GB RAM offers smoother everyday use but is still minimal for modern apps. Ideally, go for 8GB or higher.
14. RAM vs SSD storage: Which should I upgrade first?
If your computer feels slow when switching tasks, upgrade RAM. If it takes forever to boot or load files, upgrade to an SSD. Many users benefit from upgrading both.
15. Single RAM vs Dual RAM: Does it matter?
Dual RAM (two sticks) runs in dual-channel mode, giving better bandwidth and performance than a single stick of the same capacity. Always match RAM sticks for best results.
16. RAM vs HDD: Which impacts performance more?
RAM has a bigger effect on multitasking and real-time speed. HDD affects load and boot times. Replacing HDD with SSD has the biggest upgrade impact overall.
17. CPU vs RAM vs SSD: Which is most important?
All three are crucial, but balance is key. A strong CPU processes instructions, RAM manages active tasks, and SSD storage speeds up access to data. If you’re unsure where to start, guides on how much does it cost to build a gaming PC can give you a clearer picture of performance vs. price.
18. RAM vs SSD for gaming: Which should I focus on?
For gaming, both matter. RAM ensures smooth performance during gameplay, while SSD reduces load times and improves responsiveness. If you’re on a budget, exploring builds like a 300 dollar gaming PC can show you how different specs impact real-world gaming.
Conclusion
RAM and SSD serve very different purposes in your computer. RAM is your system’s short-term memory, handling active tasks and multitasking speed. SSD is long-term storage, keeping your files and operating system accessible even when the power is off.
If your PC feels slow when switching apps, more RAM can help. If it struggles to boot or load programs, an SSD upgrade makes the biggest difference. For the best performance, a balance of both is essential.
When planning a gaming setup, budget matters as much as performance. Some users opt for a refurbished gaming PC for savings, while others look into a prebuilt gaming PC under $600 or even a gaming PC under 500 to get started. Whatever you choose, understanding the role of RAM and SSD ensures your system feels fast, responsive, and future-ready.
Spread the word
.svg)