Ergonomic Injuries and How to Prevent Them from Occurring
Table of Contents
Ergonomic injuries in the workplace are a significant concern, impacting employees' health and productivity. As industries evolve, so do the challenges of maintaining safety. From office setups to physical labor environments, understanding and addressing some common ergonomic injury causes can make a significant difference in workforce health.
This article will discuss the crucial aspects of preventing an ergonomic injury.
What is an Ergonomic Workplace Injury?
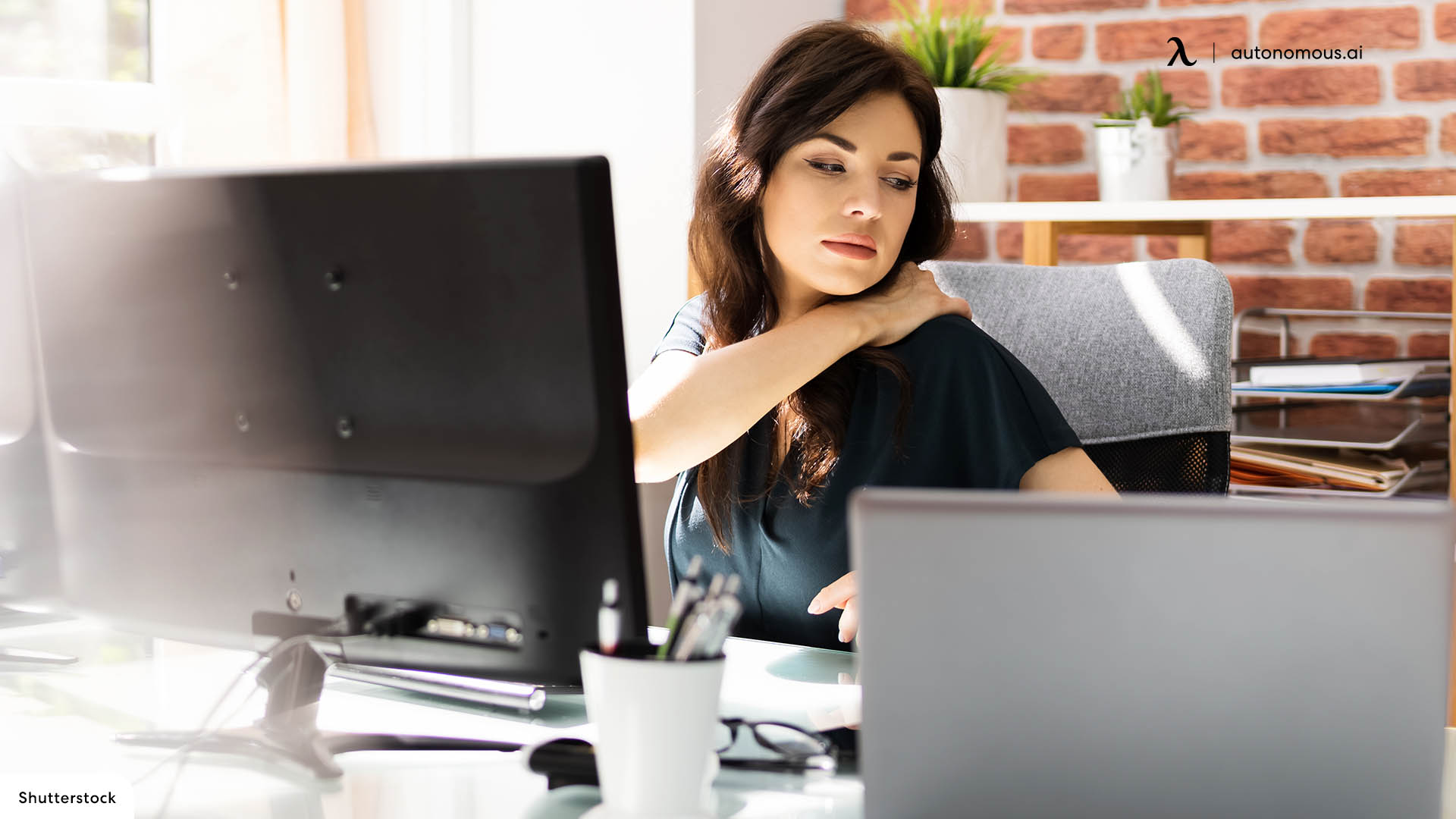
An ergonomic workplace injury refers to harm or disorders affecting the musculoskeletal system, including muscles, tendons, nerves, and joints, caused by poor workplace design or improper use of equipment. These injuries arise from ergonomic hazards, such as poorly designed workstations or repetitive tasks, leading to musculoskeletal disorders that can cause severe discomfort and long-term health issues.
Common ergonomic injury symptoms include numbness, tingling, unexplained weakness, soreness or sharp pain, stiffness, and swelling, predominantly in the back, hands, arms, wrists, elbows, neck, and shoulders.
Early recognition and treatment of these symptoms are crucial to prevent them from becoming chronic or more severe. Effective ergonomic practices, like proper workstation adjustments and use of supportive furniture, play a vital role in mitigating these injuries.
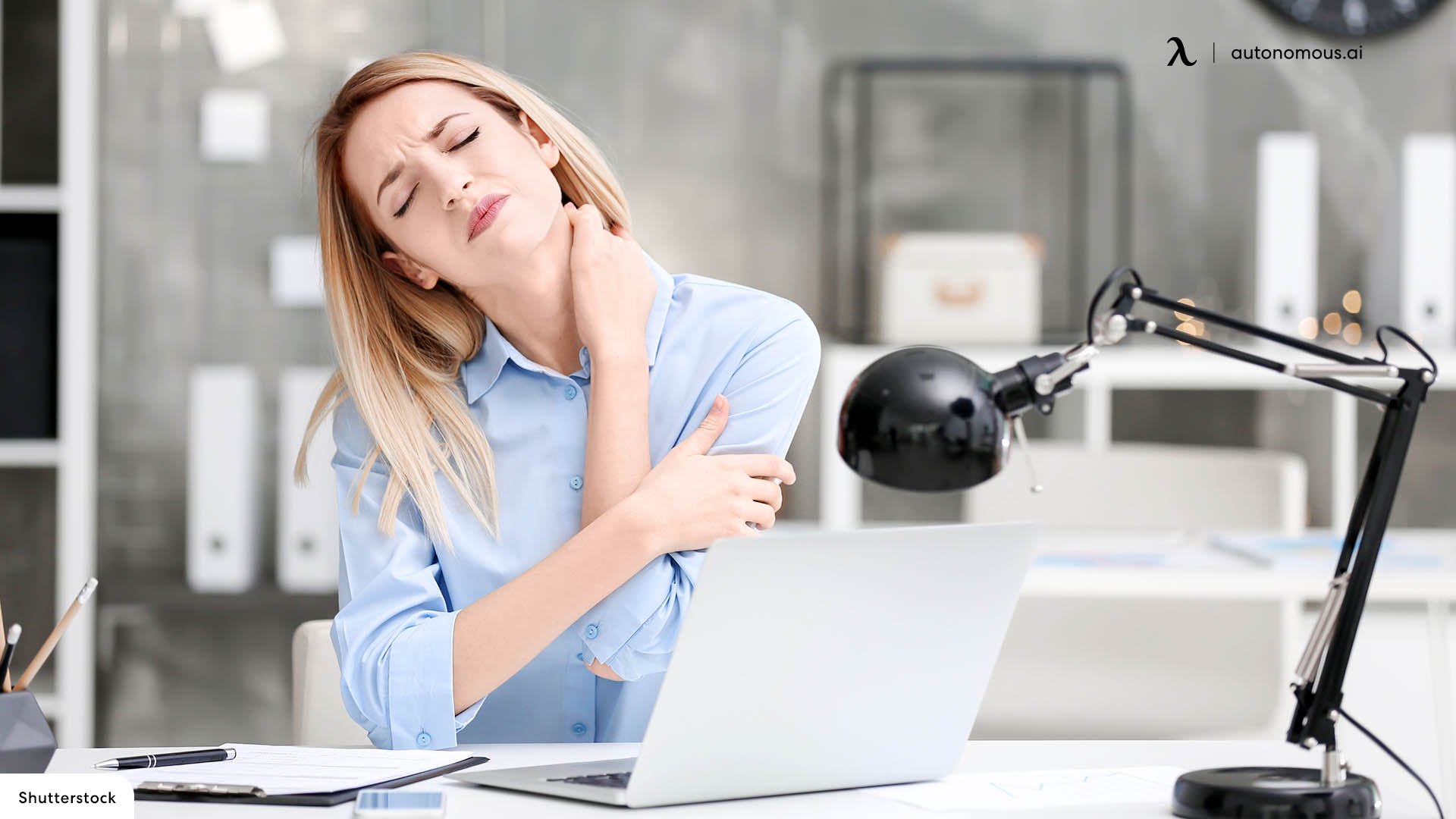

Different Types of Ergonomic Injuries
Key types include the following:
- Cumulative Trauma Disorders (CTDs): These develop over time due to repetitive stress without adequate recovery. Common CTDs include tendinitis and bursitis, often resulting from tasks that involve repetitive motion, such as typing or assembly line work.
- Repetitive Strain Injuries (RSIs): RSIs are specifically caused by repeating the same motions frequently. They affect tendons, muscles, and nerves, leading to conditions like carpal tunnel syndrome, which results from repetitive wrist movements and improper hand positions during activities like typing or using a mouse.
- Musculoskeletal Disorders (MSDs): This broad category includes injuries affecting the muscles, bones, tendons, and other soft tissues. Examples include back pain from poor posture or heavy lifting and neck strain from improper monitor height.
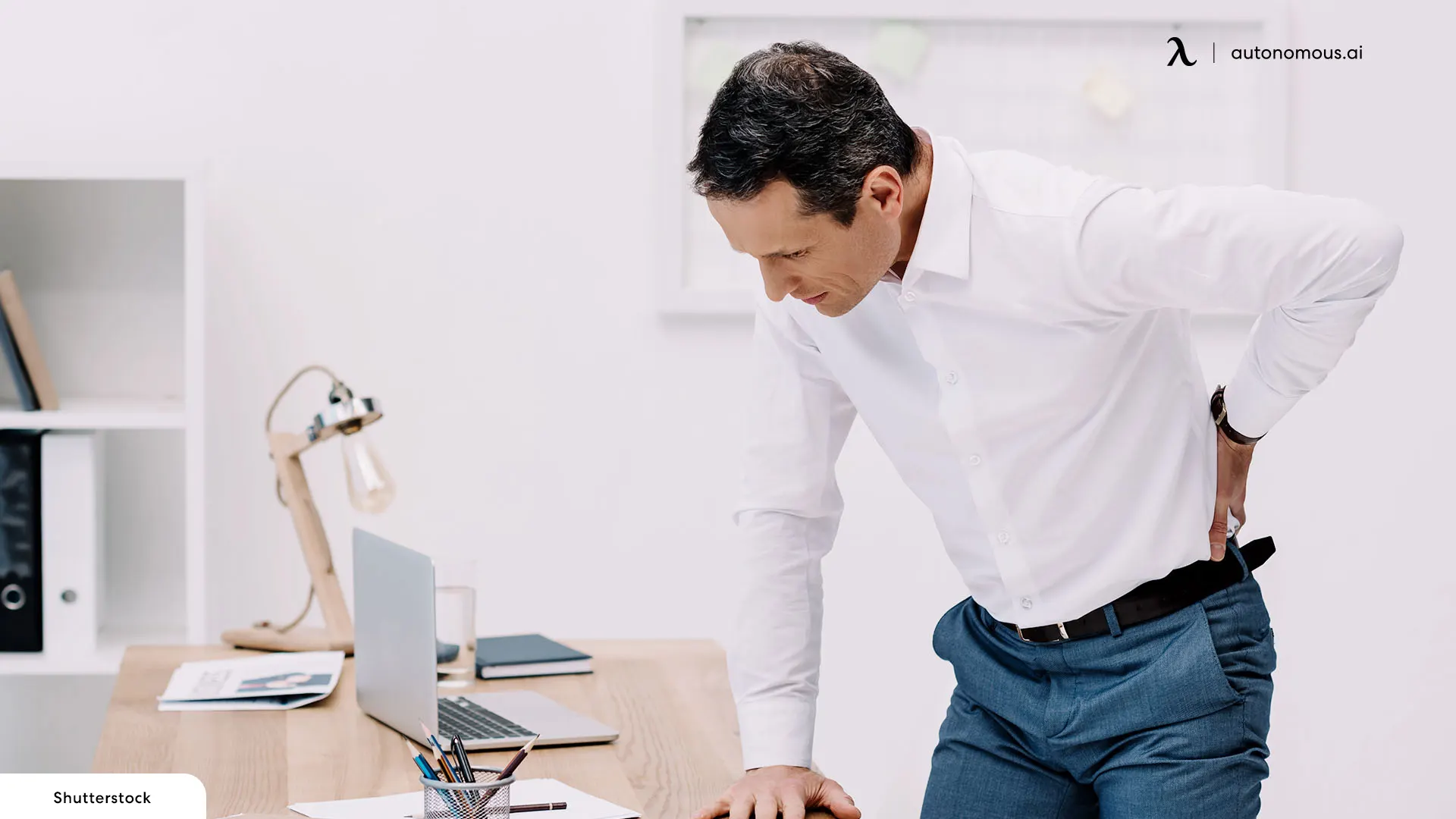

Who is Most at Risk of Developing Ergonomic Injury?
Individuals most at risk of developing ergonomic injuries include those engaged in repetitive tasks, those who maintain awkward postures for extended periods, and those who exert excessive force during their work. Workers in occupations such as manufacturing, assembly lines, data entry, and construction are particularly susceptible due to the repetitive nature and physical demands of these jobs.
Additionally, employees who use poorly designed workstations or tools, or who lack proper ergonomic training, face a higher risk. Age can also be a factor, as older workers might have decreased physical resilience, making them more prone to injuries. Furthermore, individuals with previous musculoskeletal issues or poor physical conditioning are at heightened risk.
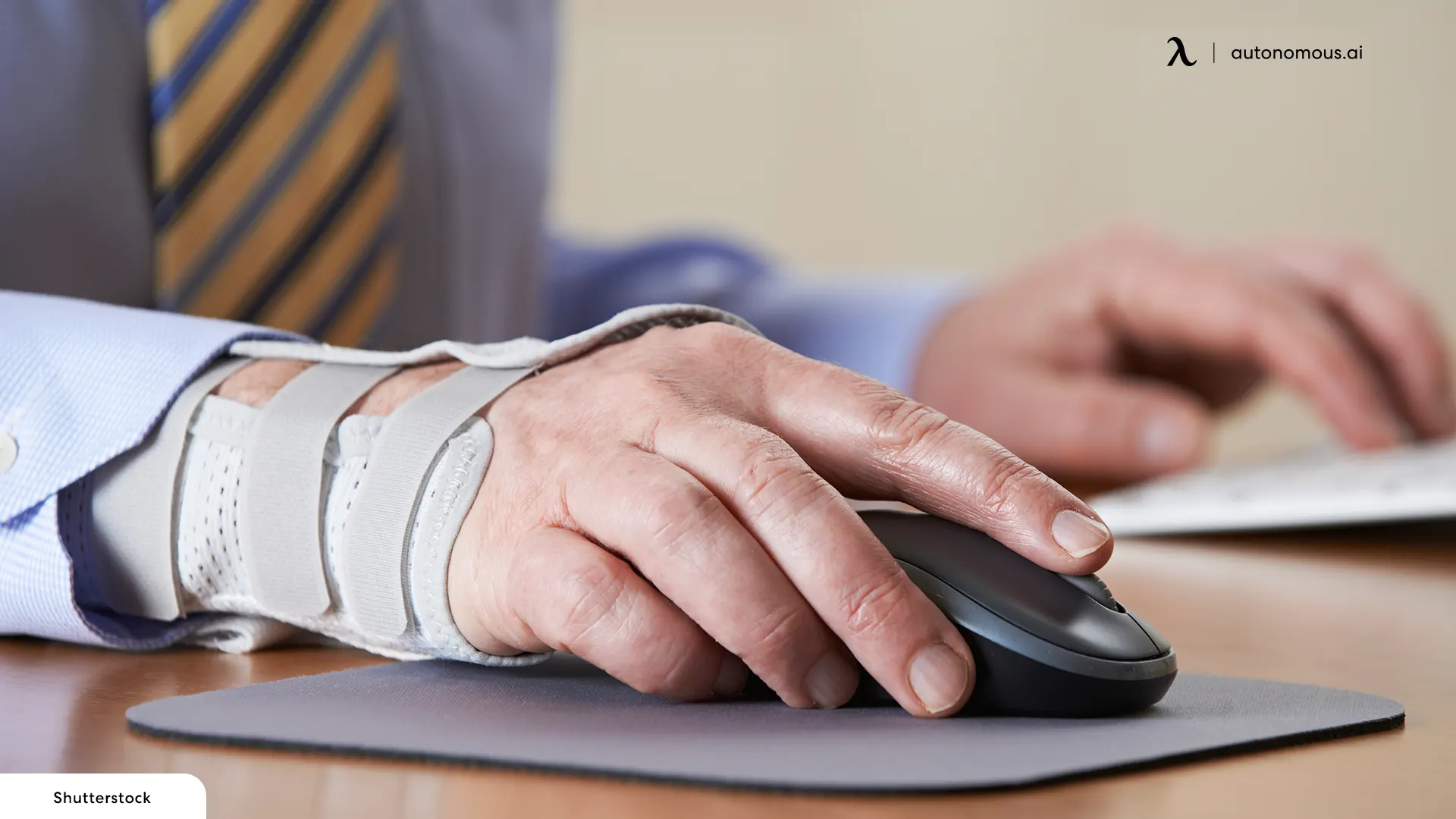

How Can Ergonomic Injuries Be Prevented?
Preventing ergonomic injuries involves a combination of proper workstation design, equipment use, and workplace practices. Ensuring that workstations are ergonomically set up, with adjustable chairs and desks, helps maintain neutral body positions and reduce strain. Using supportive office accessories like footrests and monitor stands can further enhance posture and comfort.
Incorporating regular breaks and encouraging movement can prevent the muscle fatigue associated with prolonged stationary positions. Job rotation and task variety help reduce the repetitive strain on specific muscle groups. Ergonomic training for employees is crucial, educating them on proper posture, lifting techniques, and the importance of adjusting their work environment.
Employers should also conduct regular ergonomic assessments to identify and mitigate risk factors. Personal protective equipment, such as wrist supports or cushioned floor mats, can provide additional support where immediate ergonomic redesigns are not possible.
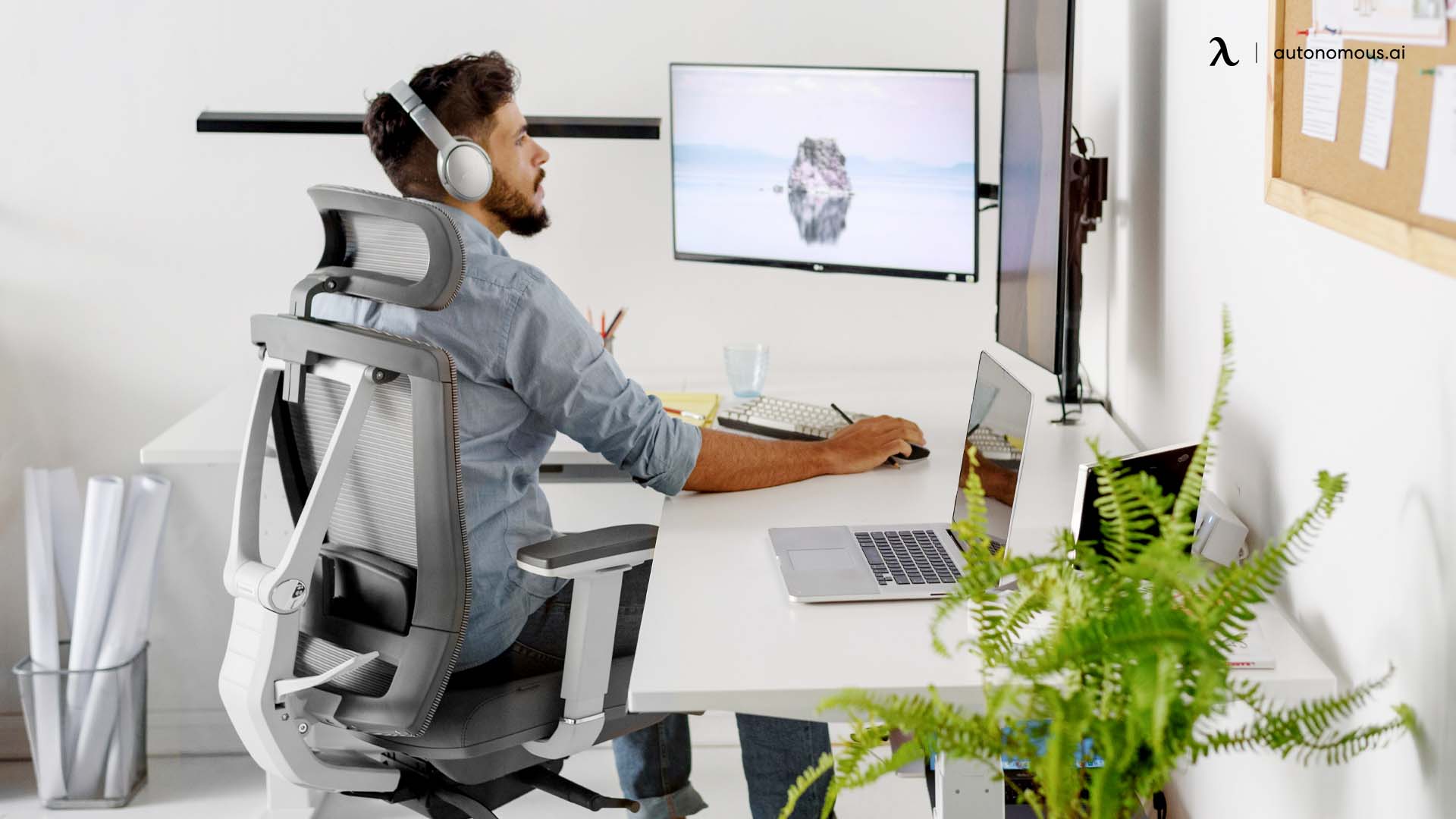

Role of Ergonomic Office Furniture in Preventing Ergonomic Injuries?
The strategic use of ergonomic office furniture can significantly mitigate ergonomic injuries.
The ergonomic desk setup diagram is essential for visualizing and implementing proper workstation adjustments. For instance, an ergonomic chair height that allows the feet to rest flat on the floor and the thighs to be parallel to the ground can prevent strain on the lower back and legs. Similarly, maintaining a proper ergonomic arm position, where elbows are close to the body and bent at a 90-degree angle, minimizes strain on the shoulders and forearms.
A standing desk offers numerous benefits, including reduced risk of back pain and improved posture. However, the proper standing desk height is crucial; it should be set so that the monitor is at eye level and the keyboard is at elbow height, promoting a neutral spine position and reducing the risk of neck and shoulder strain.
Accessories, such as footrests, monitor stands, and document holders, enhance ergonomic setups by ensuring that all elements of the workstation promote neutral body positions. For example, a footrest can help maintain proper leg alignment when the chair height is adjusted for optimal arm positioning.
Ergonomic chairs, including those designed for cross-legged sitting, are integral to preventing injuries. An ergonomic cross-legged chair supports various sitting positions, which can alleviate the strain from traditional seated postures. These chairs often feature adjustable components that accommodate different body sizes and shapes, ensuring that users can find a comfortable and supportive sitting position.
The holistic approach to workplace ergonomics involves not only individual furniture pieces but also a comprehensive understanding of standing desk ergonomics and the integration of various ergonomic principles. Employers should provide training on proper workstation setup and encourage regular breaks to reduce the risk of injuries associated with prolonged repetitive tasks.

Conclusion
Early detection of an ergonomic injury allows for timely intervention, reducing the severity and long-term impact. Implementing ergonomic injury prevention measures, such as proper workstation setup and regular breaks, is vital in mitigating risks.
Computer ergonomic injuries, in particular, highlight the importance of maintaining good posture and ergonomic practices in our increasingly digital work environments.
Spread the word
.svg)