
Calorie Expenditure: Meaning, Calculation & How to Burn More Calories
Table of Contents
Understanding calorie expenditure is key to managing weight, improving fitness, and optimizing energy levels. But what does calorie expenditure mean? Simply put, it refers to the number of calories your body burns throughout the day. This includes everything from essential functions like breathing and digestion to physical activity and exercise.
In this guide, we’ll break down what is calorie expenditure, how to calculate it, and ways to maximize your daily calorie expenditure for better health and fitness.
What Is Calorie Expenditure?
Calorie expenditure meaning refers to the total amount of energy your body uses daily. This energy is measured in calories, which are derived from food and used to support essential bodily functions, movement, and physical activity.
There are three main components of calorie expenditure per day:
- Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR) – The calories burned at rest to maintain vital functions like breathing, circulation, and cell production.
- Thermic Effect of Food (TEF) – The energy required to digest, absorb, and metabolize nutrients.
- Physical Activity Energy Expenditure (PAEE) – Calories burned through movement, including exercise and daily activities.
Average Calorie Expenditure Per Day
The average calorie expenditure per day varies based on factors like age, gender, weight, muscle mass, and activity level. Below is a general breakdown:
Category | Men (Calories/Day) | Women (Calories/Day) |
Sedentary | 2,000–2,400 | 1,600–2,000 |
Moderately Active | 2,400–2,800 | 2,000–2,400 |
Very Active | 2,800–3,200 | 2,400–2,800 |
These numbers represent a rough estimate and can be adjusted based on individual metabolism and lifestyle. Understanding the difference between active calories and total calories can help fine-tune your daily calorie goals. Additionally, knowing how active calories compare to resting calories can give you a clearer picture of how your body burns energy throughout the day.
While tracking calorie expenditure per day, many wonder if calories in vs. calories out is the ultimate formula for weight loss. While the concept is generally true, there are important myths and nuances to consider.

How to Calculate Daily Calorie Expenditure
If you’re wondering how to calculate daily calorie expenditure, follow these steps:
1. Calculate Your BMR
Use the Mifflin-St Jeor Equation, one of the most accurate methods:
- Men: BMR = (10 × weight in kg) + (6.25 × height in cm) – (5 × age in years) + 5
- Women: BMR = (10 × weight in kg) + (6.25 × height in cm) – (5 × age in years) – 161
2. Adjust for Activity Level
Multiply your BMR by the appropriate activity factor:
Activity Level | Multiplier |
Sedentary (little or no exercise) | 1.2 |
Lightly active (light exercise 1-3 days/week) | 1.375 |
Moderately active (moderate exercise 3-5 days/week) | 1.55 |
Very active (hard exercise 6-7 days/week) | 1.725 |
Super active (intense exercise or physical job) | 1.9 |
Example: If a 30-year-old woman weighs 65 kg, is 165 cm tall, and exercises moderately, her BMR would be:
(10 × 65) + (6.25 × 165) – (5 × 30) – 161 = 1,402 calories
Now, multiplying by 1.55 (moderate activity): 1,402 × 1.55 = 2,173 calories/day
Caloric Expenditure Chart for Common Activities
Different activities burn varying amounts of calories. Below is a caloric expenditure chart for a 155-lb (70 kg) person performing different activities for 30 minutes:
Activity | Calories Burned (30 min) |
Walking (3.5 mph) | 149 |
Running (6 mph) | 372 |
Cycling (moderate pace) | 298 |
Swimming (moderate) | 223 |
Yoga | 149 |
Strength Training | 112 |
Sitting | 40 |
More intense activities lead to higher daily calorie expenditure, making it important to track your active calorie calculation to get an accurate estimate. If you're wondering how many active calories you should burn per day, it depends on your goals and lifestyle.
For those using a StairMaster for workouts, you may want to know how to calculate calories burned on a StairMaster. Similarly, if you're focused on step-based movement, you might be curious about how many calories 10,000 steps burn.

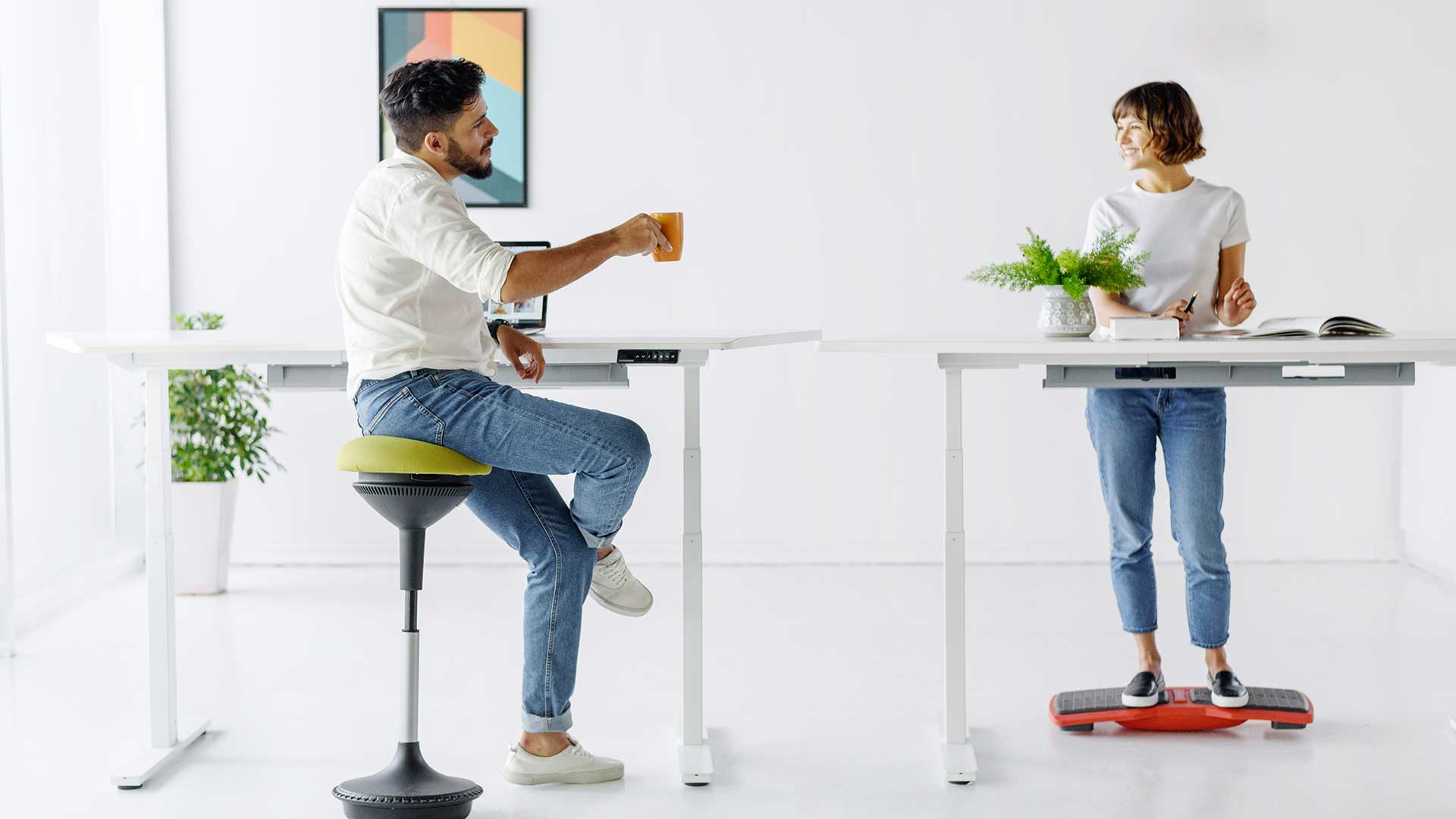
Boosting Calorie Expenditure at Work with Ergonomic Furniture
Most people spend 8+ hours a day sitting, which limits daily calorie expenditure. The good news? Simple ergonomic changes can increase calorie burn and improve overall health.
1. Standing Desks: Burn More Calories While You Work
Using a standing desk instead of sitting all day can significantly impact calorie expenditure per day. Studies suggest that standing burns 20–50 more calories per hour compared to sitting. Over a full workday, that adds up to an extra 100–250 calories burned—equivalent to a short walk. If you're curious about the exact difference, check out this comparison of calories burned standing vs. sitting.
Ways to Maximize Your Standing Desk for Calorie Burn
- Alternate Between Sitting and Standing: Aim for a 50/50 split between standing and sitting throughout the day.
- Use a Balance Board or Anti-Fatigue Mat: Engages your core and leg muscles, increasing calorie expenditure.
- Take Micro-Movement Breaks: Shift your weight, do light stretches, or march in place while working.
Wondering does a standing desk burn calories? Research confirms that it does. Additionally, there are ways to burn calories at work—even if you have a desk job.

2. Ergonomic Stools: Engage Your Core for Passive Calorie Burning
Unlike traditional chairs, an ergonomic stool encourages active sitting, meaning your body naturally moves to maintain balance. This helps engage core muscles, improve posture, and slightly increase calorie expenditure. If you're unfamiliar with active sitting, it's a method of seating that keeps your muscles engaged even while working.
Why an Ergonomic Stool Helps:
- Promotes micro-movements that activate core and leg muscles.
- Reduces sedentary behavior, which is linked to lower metabolism.
- Encourages better posture, preventing fatigue that leads to excessive sitting.
Ways to Stay Active While Sitting:
- Use Dynamic Seating: Chairs with a slight recline and movement features encourage subtle muscle engagement. Check out these best active chairs for active sitting for more options.
- Practice Seated Exercises: Try ankle rotations, seated marches, or shoulder rolls to keep blood circulation active.
- Adjust Posture Frequently: Avoid staying in one fixed position for too long. Learn more about how to stay active at your desk with simple movements throughout the day.

FAQs
What is the difference between calorie expenditure and calorie deficit?
Calorie expenditure refers to the total number of calories your body burns daily through metabolism, digestion, and physical activity.
Calorie deficit occurs when you consume fewer calories than your daily calorie expenditure, leading to weight loss.
Can you have high calorie expenditure but not be in a calorie deficit?
Yes! If you burn a lot of calories through exercise or an active lifestyle but eat the same or more than you burn, you won’t be in a deficit and won’t lose weight.
What is the average calorie expenditure per day?
Men burn around 2,000–3,000 calories/day, while women burn 1,600–2,400 calories/day, depending on activity levels.
Do men and women burn calories differently?
Yes, men typically have higher BMR due to greater muscle mass, meaning they burn more calories at rest than women.
Do taller people burn more calories?
Generally, yes. Taller individuals have more body surface area and muscle mass, requiring more energy to function.
Does muscle burn more calories than fat?
Yes. Muscle tissue burns more calories at rest than fat, which is why strength training helps increase daily calorie expenditure.
Can you burn calories while sleeping?
Yes, your body continues to burn calories for essential functions like breathing, circulation, and cell repair. The Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR) represents the calories burned at rest, including while you sleep. If you're curious about how many calories you burn doing nothing—whether resting, sitting, or sleeping—this guide provides a breakdown based on different factors like age, weight, and metabolism.
Can drinking water increase calorie expenditure?
Yes, drinking water temporarily boosts metabolism by activating thermogenesis, especially cold water, which requires energy to warm up in the body.
Conclusion
Your calorie expenditure per day depends on several factors, including metabolism, diet, and lifestyle. Understanding how to calculate calorie expenditure helps you make informed choices about diet and exercise.
Whether your goal is weight loss, muscle gain, or maintaining a healthy lifestyle, optimizing your daily calorie expenditure through exercise and smart habits can make a difference. If you're tracking your intake and output, using a calorie tracker can help you stay on top of your progress.
For those looking to gain weight strategically, a weight gain calorie calculator can determine the ideal surplus needed to build muscle effectively. If your focus is on burning more calories at work, check out these ways to lose weight while working without disrupting your productivity.
Stay connected with us!
Subscribe to our weekly updates to stay in the loop about our latest innovations and community news!
Interested in a Link Placement?
Spread the word
.svg)
.svg)


/https://storage.googleapis.com/s3-autonomous-upgrade-3/production/ecm/230914/bulk-order-sep-2023-720x1200-CTA-min.jpg)

/https://storage.googleapis.com/s3-autonomous-upgrade-3/production/ecm/230824/Amanda-8035f52a-7230-4c31-9bda-626fd7c392bf.jpg)